Note that isotopic atomic species of a given element is uniquely identified by the mass number A, also called atomic mass number, which is the number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in an atomic nucleus. On 1 May 2014 a paper published in Phys. Khuyagbaatar and others states the superheavy element with atomic number Z = 117 (ununseptium) was produced as an evaporation residue in the 48 Ca and 249 Bk fusion reaction at the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA at GSI Darmstadt, Germany.
Atomic Mass Of Elements Pdf
The average atomic mass of an element is the sum of the masses of its isotopes, each multiplied by its natural abundance.
Atomic Mass Of Elements Definition
Learning Objectives
Patented Technology uses Fine-line Brush for Sharp Edges In this video, Accubrush Inventor Chris Pyles explains how the patented combination of a roller, shield, and brush work together to quickly paint straight lines along the edges of walls and along trim. Roller holds a lot of paint, allowing you to paint 6. Brush tools are general more designed for building, sculpting, and painting than the general utility tools.Like the rest of the tools, they are bound to an item by using the command, and are activated by right-clicking (or left clicking, for those with two actions). A foam paint brush is just the right tool for arts and crafts. Thick-handled styles are perfect for kids to grab onto — just keep them away from the walls. Paint brush brush size. Whichever way you decide to carry the paint around, here's the way you properly load a paintbrush: Dip the brush directly into the paint up to 1/3 of the length of the bristles. This stops the brush from being overloaded with paint and prevents dripping. Tap both sides of the brush lightly against the side of. 6,198 Best Paint Free Brush Downloads from the Brusheezy community. Paint Free Brushes licensed under creative commons, open source, and more!
- Calculate the average atomic mass of an element given its isotopes and their natural abundance
Key Points
- An element can have differing numbers of neutrons in its nucleus, but it always has the same number of protons. The versions of an element with different neutrons have different masses and are called isotopes.
- The average atomic mass for an element is calculated by summing the masses of the element’s isotopes, each multiplied by its natural abundance on Earth.
- When doing any mass calculations involving elements or compounds, always use average atomic mass, which can be found on the periodic table.
Key Terms
- mass number: The total number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus.
- natural abundance: The abundance of a particular isotope naturally found on the planet.
- average atomic mass: The mass calculated by summing the masses of an element’s isotopes, each multiplied by its natural abundance on Earth.
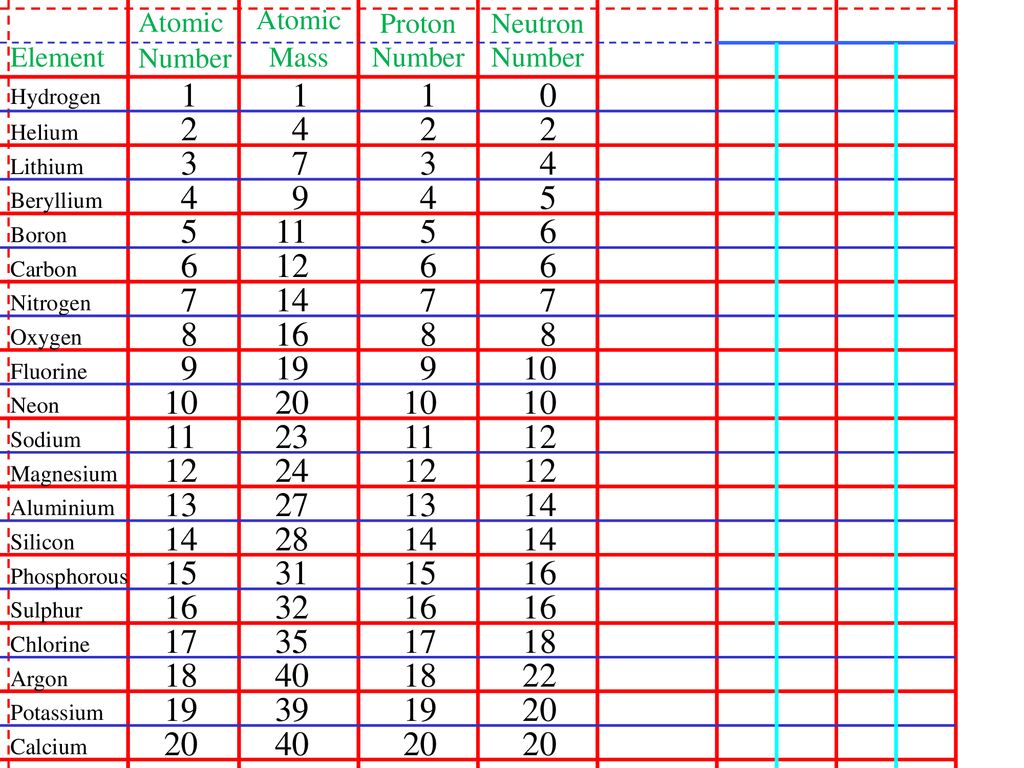
The atomic number of an element defines the element’s identity and signifies the number of protons in the nucleus of one atom. For example, the element hydrogen (the lightest element) will always have one proton in its nucleus. The element helium will always have two protons in its nucleus.
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element can, however, have differing numbers of neutrons in their nucleus. For example, stable helium atoms exist that contain either one or two neutrons, but both atoms have two protons. These different types of helium atoms have different masses (3 or 4 atomic mass units ), and they are called isotopes. For any given isotope, the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus is called the mass number. This is because each proton and each neutron weigh one atomic mass unit (amu). By adding together the number of protons and neutrons and multiplying by 1 amu, you can calculate the mass of the atom. All elements exist as a collection of isotopes. The word ‘isotope’ comes from the Greek ‘isos’ (meaning ‘same’) and ‘topes’ (meaning ‘place’) because the elements can occupy the same place on the periodic table while being different in subatomic construction.
Calculating Average Atomic Mass
The average atomic mass of an element is the sum of the masses of its isotopes, each multiplied by its natural abundance (the decimal associated with percent of atoms of that element that are of a given isotope).
Average atomic mass = f1M1 + f2M2 +… + fnMnwhere f is the fraction representing the natural abundance of the isotope and M is the mass number (weight) of the isotope.
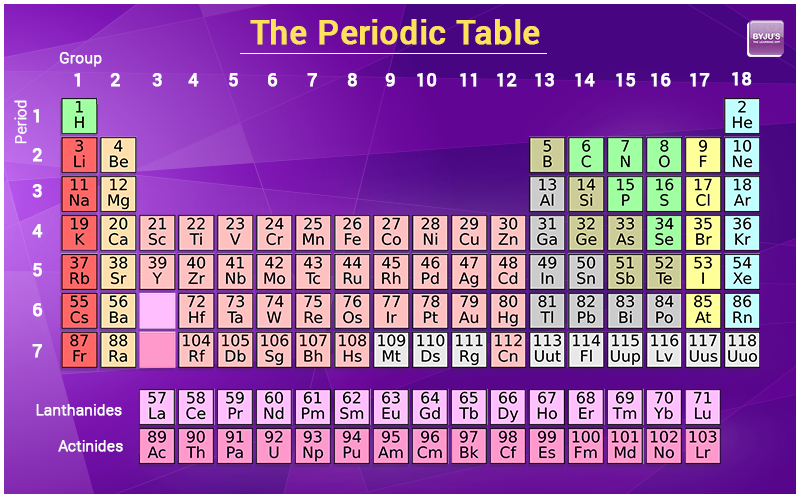
The average atomic mass of an element can be found on the periodic table, typically under the elemental symbol. When data are available regarding the natural abundance of various isotopes of an element, it is simple to calculate the average atomic mass.
- For helium, there is approximately one isotope of Helium-3 for every million isotopes of Helium-4; therefore, the average atomic mass is very close to 4 amu (4.002602 amu).
- Chlorine consists of two major isotopes, one with 18 neutrons (75.77 percent of natural chlorine atoms) and one with 20 neutrons (24.23 percent of natural chlorine atoms). The atomic number of chlorine is 17 (it has 17 protons in its nucleus).
To calculate the average mass, first convert the percentages into fractions (divide them by 100). Then, calculate the mass numbers. The chlorine isotope with 18 neutrons has an abundance of 0.7577 and a mass number of 35 amu. To calculate the average atomic mass, multiply the fraction by the mass number for each isotope, then add them together.
Average atomic mass of chlorine = (0.7577 ⋅⋅ 35 amu) + (0.2423 ⋅⋅ 37 amu) = 35.48 amu
Another example is to calculate the atomic mass of boron (B), which has two isotopes: B-10 with 19.9% natural abundance, and B-11 with 80.1% abundance. Therefore,
Average atomic mass of boron = (0.199⋅⋅10 amu) + (0.801⋅⋅11 amu) = 10.80 amu
Atomic Mass Of Elements Pdf


Whenever we do mass calculations involving elements or compounds (combinations of elements), we always use average atomic masses.

LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SPECIFIC ATTRIBUTION
- ionic bond. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: en.wiktionary.org/wiki/ionic_bond. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest..ol11448/latest. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Biochemistry/Metabolism and energy. Provided by: Wikibooks. Located at: en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Biochem..%23Ionic_bonds. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- ion. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: en.wiktionary.org/wiki/ion. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- OpenStax College, Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: The Building Blocks. October 16, 2013. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest..e_02_01_10.jpg. License: CC BY: Attribution
- OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest..ol11448/latest. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Biochemistry/Metabolism and energy. Provided by: Wikibooks. Located at: en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Biochem..%23Ionic_bonds. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- dipole. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: en.wiktionary.org/wiki/dipole. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- covalent bond. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: en.wiktionary.org/wiki/covalent_bond. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- hydrogen bond. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: en.wiktionary.org/wiki/hydrogen_bond. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- OpenStax College, Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: The Building Blocks. October 16, 2013. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest..e_02_01_10.jpg. License: CC BY: Attribution
- OpenStax College, Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: The Building Blocks. October 16, 2013. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest..e_02_01_11.jpg. License: CC BY: Attribution
- ATP structure. Provided by: Wikimedia. Located at: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi.._structure.svg. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Hydrogen bond. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_bond. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- electronegativity. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: en.wiktionary.org/wiki/electronegativity. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- intermolecular. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: en.wiktionary.org/wiki/intermolecular. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- OpenStax College, Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: The Building Blocks. October 16, 2013. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest..e_02_01_10.jpg. License: CC BY: Attribution
- OpenStax College, Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: The Building Blocks. October 16, 2013. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest..e_02_01_11.jpg. License: CC BY: Attribution
- ATP structure. Provided by: Wikimedia. Located at: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi.._structure.svg. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- File:3D model hydrogen bonds in water.svg - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/w/index.php?..ter.svg&page=1. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Water drops on green leaf. Provided by: Wikimedia Commons. Located at: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi..green_leaf.jpg. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Avogadro's number and the mole. Provided by: Steve Lower's Website. Located at: http://www.chem1.com/acad/webtext/intro/int-2.html#SEC2. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Mole (unit). Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Mole_(unit). License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Avogadro constant. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Avogadro_constant. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- mole. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: en.wiktionary.org/wiki/mole. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- OpenStax College, Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: The Building Blocks. October 16, 2013. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest..e_02_01_10.jpg. License: CC BY: Attribution
- OpenStax College, Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: The Building Blocks. October 16, 2013. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest..e_02_01_11.jpg. License: CC BY: Attribution
- ATP structure. Provided by: Wikimedia. Located at: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi.._structure.svg. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- File:3D model hydrogen bonds in water.svg - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/w/index.php?..ter.svg&page=1. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Water drops on green leaf. Provided by: Wikimedia Commons. Located at: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi..green_leaf.jpg. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- The Mole, Avogadro. Located at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TqDqLmwWx3A. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright. License Terms: Standard YouTube license
- Avogadro Amedeo. Provided by: Wikimedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Avogadr..dro_Amedeo.jpg. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Introductory Chemistry Online/Measurements and Atomic Structure. Provided by: Wikibooks. Located at: en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Introdu..omic_Structure. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Atomic mass. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Atomic_mass. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Average atomic mass. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Average_atomic_mass. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- natural abundance. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/natural%20abundance. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Boundless. Provided by: Boundless Learning. Located at: www.boundless.com//biology/de..atomic-mass--2. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- isotope. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: en.wiktionary.org/wiki/isotope. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- mass number. Provided by: Wiktionary. Located at: en.wiktionary.org/wiki/mass_number. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- OpenStax College, Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: The Building Blocks. October 16, 2013. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest..e_02_01_10.jpg. License: CC BY: Attribution
- OpenStax College, Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: The Building Blocks. October 16, 2013. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest..e_02_01_11.jpg. License: CC BY: Attribution
- ATP structure. Provided by: Wikimedia. Located at: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:ATP_structure.svg. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- File:3D model hydrogen bonds in water.svg - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:3D_model_hydrogen_bonds_in_water.svg&page=1. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Water drops on green leaf. Provided by: Wikimedia Commons. Located at: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Fi..green_leaf.jpg. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- The Mole, Avogadro. Located at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TqDqLmwWx3A. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright. License Terms: Standard YouTube license
- Avogadro Amedeo. Provided by: Wikimedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Avogadr..dro_Amedeo.jpg. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- File:Stylised Lithium Atom.svg - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: en.Wikipedia.org/w/index.php?..tom.svg&page=1. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
